- Give correct names and symbols for common substances
- Construct word and balanced symbol equations
- Describe how atoms join (simply)
Friday 25 January 2013
Chemical Fundamentals
You need to be able to:
Thursday 24 January 2013
C1a Making Crude Oil Useful
You need to be able to:
- Describe the composition of crude oil
- Explain how the fractional distillation of crude oil works
- Explain the cracking of fractions
- Lots of notes on crude oil and making it useful
 GCSE Notes from Doc Brown
GCSE Notes from Doc Brown Videos and simulations on crude oil and its products
Videos and simulations on crude oil and its products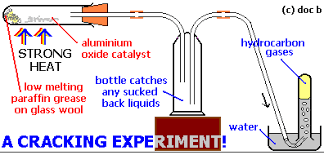
- Cracking crude oil notes
Wednesday 23 January 2013
C1b Using Carbon Fuels
You need to be able to:
- Evaluate fuels for a particular purpose
- Explain the complete combustion of hydrocarbon fuels
- Explain the incomplete combustion of hydrocarbon fuels
Tuesday 22 January 2013
C1c Clean Air
You need to be able to:
- Describe the composition and formation of today's atmosphere
- Explain why it is important to control atmospheric pollution
- Describe how a catalytic converter works



- Atmospheric evolution from NASA
- BBC Bitesize notes 1 and 2
- The story of the catalytic converter by BASF
Monday 21 January 2013
C1d Making Polymers
You need to be able to:
- Describe saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons
- Explain how to make an addition polymer

 Alkane, alkene and alkyne (triple bond) quiz - alkenes not on the exam!
Alkane, alkene and alkyne (triple bond) quiz - alkenes not on the exam!- Monomer to polymer interactive model
 What, you guys again?!
What, you guys again?!
Sunday 20 January 2013
C1e Designer Polymers
You need to be able to:
- Explain links between polymer properties and uses
- Explain properties of Gore-Tex(R) and nylon
- Explain issues with the use of polymers
- Designer polymers notes from the BBC (look at all 4 pages)

- Examples of designer polymers and issues with polymers
Saturday 19 January 2013
C1f Food
You need to be able to
- Explain what cooking does to foods and why this makes them easier to digest
- Explain the action of emulsifiers
- Construct balanced equations showing how baking powder (sodium hydrogen carbonate) works, and how you can test for the gas made
Friday 18 January 2013
C1g Smells
You need to be able to
- Describe and explain the formation and properties of esters in synthetic perfumes
- Explain how esters can be used as solvents (or why water won't remove nail polish)
- Explain the need to test cosmetics, and opinions surrounding testing on animals
Thursday 17 January 2013
C1h Paints and Pigments
You need to be able to:
- Describe the ingredients in and explain the structure of paints (colloids)
- Explain how oil pains and how emulsion paints dry
- Describe and explain the uses of thermochromatic and phosphorescent pigments
- Paints and pigments notes from Bitesize
- Paints video...
- And another...
- Watching paint dry animation and notes
Wednesday 16 January 2013
C2a The Structure of the Earth
You need to be able to:
- Describe the properties of the layers of the Earth and the problems in studying it
- Describe the development and the theory of plate tectonics
- Describe the action of volcanoes
- Lots of visualisations - scroll down to "chapter 8 plate tectonics"
- Wegener's Theory - notes from BBC Bitesize

- Interactive map of active volcanoes
 Information and videos on volcano types
Information and videos on volcano types- Composite vs shield volcano video
- Lots of notes...


Tuesday 15 January 2013
C2b Construction Materials
You need to be able to:
- Explain the formation, properties and uses of marble, granite and limestone
- Construct a balanced symbol equation for the decomposition of limestone
- Compare and contrast the manufacture and properties of cement, concrete and reinforced concrete
 Lots of notes and web links on rock types and rock cycle
Lots of notes and web links on rock types and rock cycle Thermal decomposition of limestone notes from the BBC
Thermal decomposition of limestone notes from the BBC- Notes from Doc Brown
Monday 14 January 2013
C2c Metals and Alloys
You need to be able to:
- Explain the extraction and purification of copper using balanced symbol equations and half equations
- Evaluate the use of metals and/or alloys for a particular use (e.g. amalgam, brass, solder, bronze, steel)
- Explain how smart alloys can be used
- Notes on electrolysis from BBC Bitesize
 Another chemistry blog with notes on electrolysis
Another chemistry blog with notes on electrolysis- Practical purification of Cu...
- Alloys notes from BBC Bitesize
Sunday 13 January 2013
C2d Making Cars
You need to be able to:
- Explain rusting using balanced symbol equations, and descriptions of ideal conditions
- Evaluate the use of aluminium, steel and other materials in the manufacture of cars
- Explain the advantages and disadvantages of recycling materials used to make cars
- Iron vs Aluminium notes from BBC Bitesize
Saturday 12 January 2013
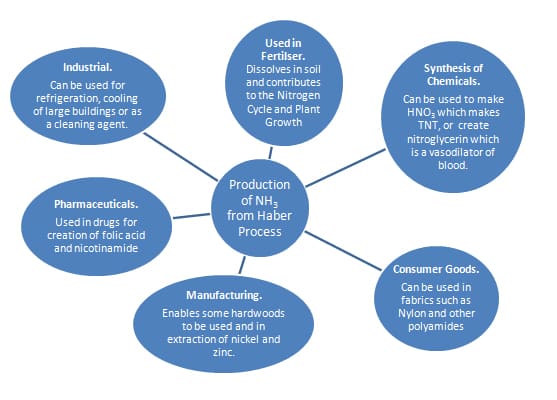
C2e Manufacturing Chemicals: Making Ammonia
You need to be able to:
- Describe how ammonia is made in the Haber Process utilising balanced symbol equations
- Explain the conditions used in the Haber process in relation to the reversible reaction and to economic considerations
- Explain why producing ammonia is important
- Make sure you can interpret graphs....


Friday 11 January 2013
C2f Acids and Bases
You need to be able to:
- Explain how neutralisation occurs
- Construct word and balanced symbol equations for the neutralisation of acids by metal oxides, metal hydroxides and metal carbonates
- Neutralisation interactive (flash required)
- High level neutralisation animation (flash required)

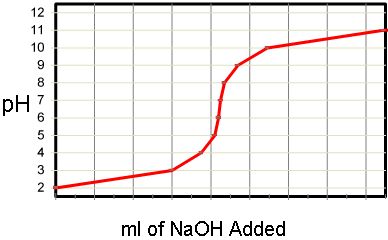
- BBC Bitesize - How to name salts
Thursday 10 January 2013
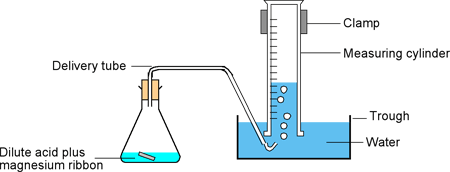
C2g Fertilisers and Crop Yields
You need to be able to:
- Explain how fertilisers increase crop yield
- Explain the pros and cons of using fertilisers (including eutrophication)
- Explain how to make a named fertiliser
- Bitesize notes on fertilisers
- Eutrophication site with cartoon explanation
- Experimental procedure and diagram for making a fertiliser
Wednesday 9 January 2013
C2h Chemicals from the Sea: Sodium Chloride
You need to be able to:
- Explain the 2 ways salt can be obtained and issues with these methods
- Explain the electrolysis of sodium chloride
- Describe the products made from sodium chloride and why these are economically important
Tuesday 8 January 2013
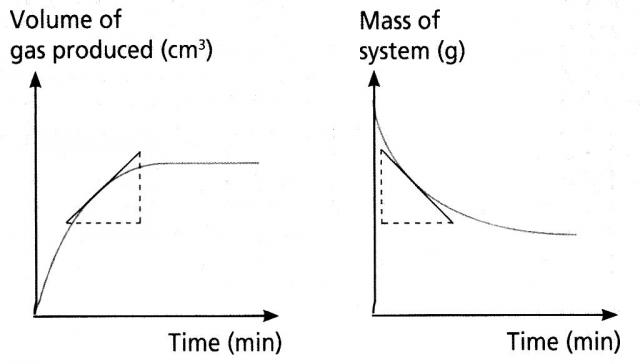
C3a - Rate of Reaction 1
You need to be able to:
- Explain the meaning of data given in g/s, g/min, cm3/s or cm3/min with regard to reaction rate
- Gather and plot reaction rate data using volumes, mass loss or reaction times
- Explain why reaction stops in terms of limiting reactant (including the idea of proportionality)
Monday 7 January 2013
C3b - Rate of Reaction 2
You need to be able to:
- Explain how collision frequency and collision energy effects the rate of reaction
- Explain in terms of particle collisions the changes in rate when pressure, concentration or temperature is altered
- Draw sketch graphs for these reactions (x axis is effect varied, y axis is reaction rate)
Sunday 6 January 2013
C3c - Rate of Reaction 3
You need to be able to:
- Explain the action of catalysts in chemical reactions (change in rate, unchanged, small amount required, specificity
- Explain in terms of collisions how altering particle size can alter reaction rate
- Explain how powder explosions can occur
- Catalysts and rate notes from Chemguide
Saturday 5 January 2013
C3d - Reacting Masses
You need to be able to:
- Use RFM and a symbol equation to show how mass is conserved in a reaction
- Calculate masses of reactants or products using RFM and symbol equations
- Explain why mass is conserved in reactions
- BBC Bitesize notes (use all 4 pages)
- Lots of RMM and RFM worked examples

Friday 4 January 2013
C3e - Percentage Yield and Atom Economy
You need to be able to:
- Recall and use equations for percentage yield and atom economy
- Calculate atom economy given a balanced symbol equation and RFM
- Explain why industrial processes aim for the highest possible percentage yield and atom economy
- How to calculate percentage yield and atom economy slides

- Bitesize notes on C3e use both pages
Thursday 3 January 2013
C3f - Energy
You need to be able to:
- Explain why a reaction is endothermic or exothermic, based on bonding
- Describe a practical method for comparing fuels
- Use equations to calculate energy transferred, mass of water heated, temperature change and energy output
- Endothermic and exothermic notes and videos
- Experimental methods from Doc Brown

- Energy equation (Q = mcdeltaT) video
Wednesday 2 January 2013
C3g - Batch or Continuous?
You need to be able to:
- Evaluate batch and continuous manufacturing processes
- Explain the process involved in developing, testing and manufacturing pharmaceutical drugs
- Describe how the purity of a compound can be established
- Bitesize notes on C3g
- Phases of drug testing

- Lab method for determining melting point
Tuesday 1 January 2013
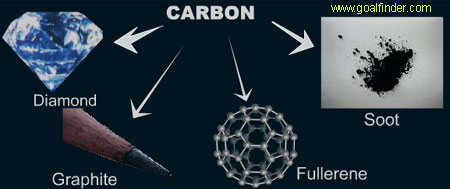
C3h - Allotropes of Carbon and Nanochemistry
You need to be able to:
- Explain the properties of three allotropes of carbon in terms of structure and bonding
- Predict and explain the properties of substances that have giant molecular structures
- Recall and explain uses of carbon allotropes and nanotubes
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)